


The industrial park has demonstrated notable economic achievements as a result of implementing key eco-industrial park (EIP) indicators, particularly those focused on sustainable and inclusive economic development.
By enabling and actively promoting the establishment of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that deliver essential services and contribute to the value chains of resident companies, the park has fostered a dynamic ecosystem of interdependent businesses.
This approach has not only improved service efficiency within the park but also generated employment opportunities and enhanced local entrepreneurship.
By implementing a cost-recovery model, the park management ensures that the services provided to residents are priced realistically, balancing affordability with operational viability. This has resulted in improved transparency, trust among stakeholders, and the ability to sustain high-quality services without external subsidies. The park’s management entity has achieved and maintained financial solvency, ensuring the sustainability of its operations and the continuous provision of core infrastructure and services. This financial stability has enabled long-term planning, reinvestment into park upgrades, and enhanced investor confidence.

In June 2024, one of the tenant companies, the largest electricity consumer in the industrial park, installed a solar power station to meet its own energy needs. This project was initiated through cooperation between GEIPP Ukraine and the UNIDO project “Industrial capacity-building, policy advice, and diagnostics for the green recovery of Ukraine, ” which is funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development of Germany.

The industrial park has made strong progress in park management by adopting a set of Eco-Industrial Park (EIP) indicators based on international standards. A dedicated park management body oversees all aspects of development, operations, and monitoring. It coordinates infrastructure, services, tenant relations, and compliance, forming the backbone of the park’s sustainability efforts.
An EIP facilitator within the management team supports implementation. A functioning monitoring system tracks annual performance in environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic output. It also helps manage key risks such as hazardous material releases, fire hazards, and natural disasters. An internal environmental control unit acts as an early-warning system, aiding in both prevention and emergency response.
All resident firms have signed contracts or charters that authorize the management body to deliver services and enforce standards. Shared services operate under a transparent, fee-based model to help achieve EIP goals like energy efficiency and waste reduction.
Programs are in place to improve energy use, especially for high-consumption tenants. The park has also set targets to increase water reuse through industrial effluent recycling and stormwater harvesting, improving both resource efficiency and cost savings.
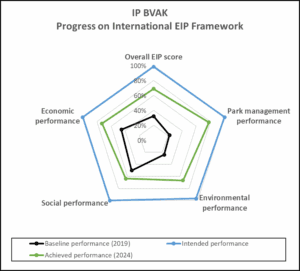
The results illustrate that IP BVAK improvement potential within the EIP context amounts to 38% provided all the prerequisites/benchmarks are achieved.
The park achieved the greatest performance in the management and environment categories due to the implementation of several EIP measures, such as: Monitoring performance and risks; Climate risk assessment; Environmental and Energy Management Systems; Heat recovery strategy. Social indicators were mostly unchanged probably due to full-scale invasion, while Economic increased with adoption of a strategy for attraction go SMEs.
Tenant companies and park management have begun developing social infrastructure to promote environmentally sustainable practices among employees.
Previously, staff were unable to use bicycles or electric vehicles due to inadequate facilities. These are now operational, supporting greener transportation options.
A dedicated specialist is overseeing the enhancement of social quality standards and ongoing improvements within the industrial park.